Table of contents
Picture a world where communicating with technology is as effortless as talking to your colleagues, friends, and family. With ChatGPT leading the way, this vision is on its way to becoming a reality.
Having seen firsthand what ChatGPT can do, it should come as no surprise that businesses are eager to understand the implications of chatbots and conversational AI for their operations and how to leverage this tech for success.
However, the widespread media buzz around this tech has blurred the lines between chatbots and conversational AI. Even though the terms are often used interchangeably, it's crucial to understand their differences to make informed decisions for your organization.
Today’s topic: chatbots vs. conversational AI. You'll leave with a better understanding of the following:
- What is a chatbot
- What is conversational AI
- The difference between chatbots and conversational AI
- Conversational AI chatbot use cases
- How to make conversational AI chatbots work for the enterprise
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a tool that can simulate human conversation and interact with users through text or voice-based interfaces.
When most people talk about chatbots, they’re referring to rules-based chatbots. Also known as toolkit chatbots, these tools rely on keyword matching and pre-determined scripts to answer the most basic FAQs.
Crucially, these bots depend on a team of engineers to build every single flow, and if a user deviates from the pre-built script, the bot will not be able to keep up.
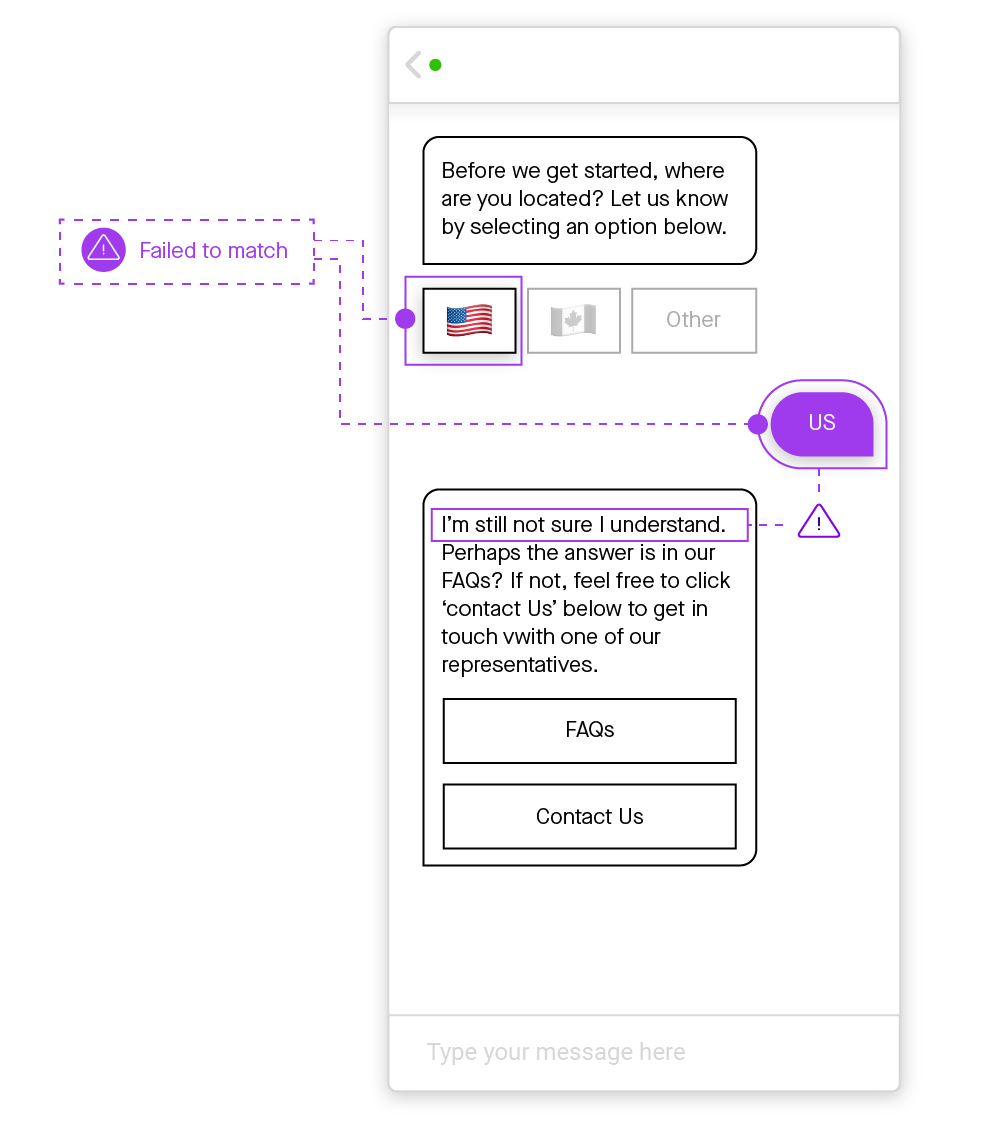 Figure 1: Rules-based chatbots with pre-scripted responses can’t keep up with unexpected user responses.
Figure 1: Rules-based chatbots with pre-scripted responses can’t keep up with unexpected user responses.
What is conversational AI?
Conversational AI is a technology that enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to natural language in a way that mimics human conversation.
For example, there are AI chatbots that offer a more natural and intuitive conversational experience than rules-based chatbots. AI chatbots use probabilistic machine learning models, natural language understanding (NLU), and conversational flow management (CFM) to understand what the user wants, hold contextual conversations, make real-time decisions, and proceed with the next actionable next steps.
Conversational AI technology can be used to power various applications beyond just chatbots. Voice assistants, like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, are examples of conversational AI tools that use voice as the primary input to interpret and respond to user requests.
Virtual assistants are another type of conversational AI that can perform tasks for users based on voice or text commands. These can be standalone applications or integrated into other systems, such as customer support chatbots or smart home systems.
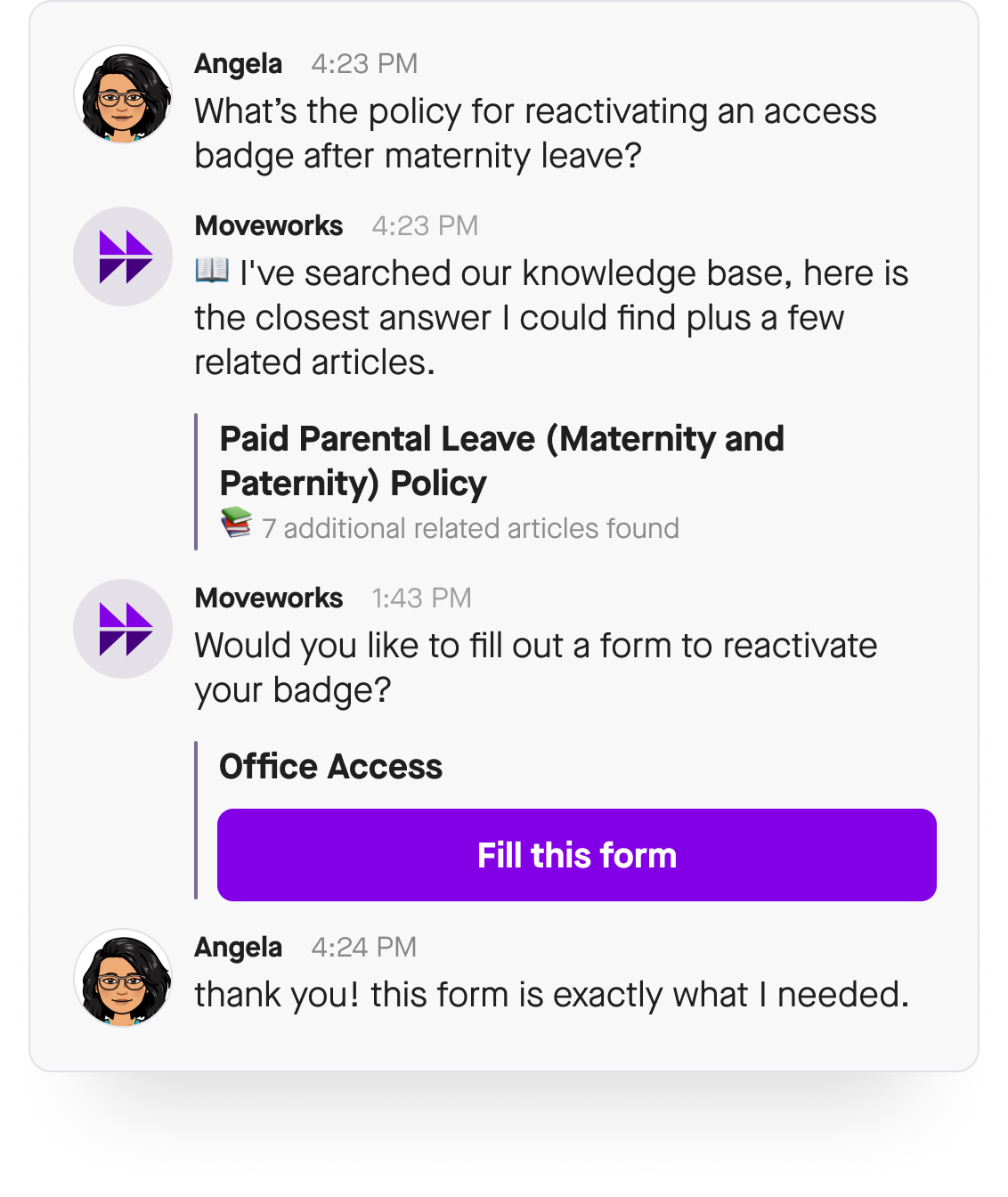 Figure 2: Conversations can go in an infinite number of directions. Conversational AI chatbots are flexible enough to keep up in the face of uncertainty.
Figure 2: Conversations can go in an infinite number of directions. Conversational AI chatbots are flexible enough to keep up in the face of uncertainty.
What are the disadvantages of conversational AI?
One of the biggest drawbacks of conversational AI is its limitation to text-only input and output. Because conversational AI is often trained on large language models — models trained on text — users were restricted to communicating through written messages and receiving responses in text form, which could be cumbersome and time-consuming.
However, with the emergence of GPT-4 and other large multimodal models, this limitation has been addressed, allowing for more natural and seamless interactions with machines. Multimodal conversational AI has been trained on more than text. As a result, conversational AI that leverages multimodal models can now process and generate various media forms, including images, audio, and video, making it more versatile and capable of meeting users' diverse communication preferences.
Chatbots vs. conversational AI: What's the difference?
Not all chatbots use conversational AI, and conversational AI can power more than just chatbots.
Think of chatbots as one possible application of conversational AI. Conversational AI is a broader concept encompassing chatbots but also includes other technologies and applications involving natural language processing and human-machine interaction.
Conversational AI can power chatbots to make them more sophisticated and effective. While rules-based chatbots can be effective for simple, scripted interactions, conversational AI offers a whole new level of power and potential. With the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions independently, conversational AI transforms how we interact with machines and help organizations unlock new efficiencies and opportunities.
What are conversational AI chatbot use cases?
As businesses increasingly turn to digital solutions for customer engagement and internal operations, chatbots and conversational AI are becoming more prevalent in the enterprise. They are hailed as the universal interface between people and digital systems.
Here are some examples of how both are currently used to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the user experience in various industries:
Chatbots in the enterprise
- Customer Service Chatbots: Many companies use chatbots to support their customers. These chatbots can handle simple queries and provide quick responses to customers.
- Employee Support Chatbots: Chatbots can be used in human resources, IT, finance, and facilities departments to provide employees with quick responses to their queries regarding policies, benefits, and troubleshooting other support-related issues.
- Sales Chatbots: Chatbots can assist sales teams by engaging with potential customers, answering their questions, and guiding them through the sales process.
Conversational AI in the enterprise
- Intelligent Personal Assistants: Some companies use conversational AI to develop intelligent personal assistants for their employees. These assistants can help employees with tasks such as scheduling meetings, setting reminders, and sending emails.
- Predictive Maintenance: Conversational AI can predict maintenance issues by analyzing data and alerting support teams before a problem occurs.
- Fraud Detection: Conversational AI can be used in financial institutions to detect fraud by analyzing customer behavior and identifying anomalies and preventing fraudulent transactions before they occur.
- Content Generation: Generate help center articles in IT, create internal communication memos for company-wide initiatives in HR, and even generate ad copy for marketing campaigns with conversational AI.
- Low-Code/No-Code Development: Conversational AI can help developers build with natural language, provide automated code review and analysis, and assist with documentation and knowledge management. Anyone can build a solution in minutes – not days, months, or years – for any use case imaginable.
How to make conversational AI that works for the enterprise
With ChatGPT and GPT-4 making recent headlines, conversational AI has gained popularity across industries due to the wide range of use cases it can help with. But simply making API calls to ChatGPT or integrating with a singular large language model won't give you the results you want in an enterprise setting.
For a conversational AI chatbot to create a lasting impact within an enterprise, it needs to connect each system and application across an enterprise, allow them to communicate seamlessly, and then take action based on the user's needs. Without deep integrations with company-specific data and the systems and apps within your organization, conversational AI use cases will be lackluster at best and downright useless at worst.
For instance, while you could ask a chatbot like ChatGPT to add you to a sales distribution list, it doesn’t have the knowledge or ability to understand and act on your request.
If, on the other hand, an enterprise uses a conversational AI chatbot specifically tailored to their organization and integrated with their tech stack, it would be able to comprehend the request and add you to the correct list.
Although the spotlight is currently on chatGPT, the challenge many companies may have and potentially continue to face is the false promise of rules-based chatbots. Many enterprises attempt to use rules-based chatbots for tasks, requiring extensive maintenance to prevent the workflows from breaking down.
It’s clear that rules-based chatbots dependent on brittle dialogue flows and scripts simply don't work, but up until recently, they were the only option available. With recent advancements in conversational AI, that's changed. Now, businesses can use this technology to build custom use cases without sacrificing the integrity of the output.
With conversational AI, building these use cases should not require significant IT resources or talent. Instead, conversational AI can help facilitate the creation of chatbot use cases and launch them live through natural language conversations without complicated dialog flows.
Conversational AI is the new way to engage in the enterprise
Conversational AI is rapidly becoming the foundation upon which the tech of the future will be built.
Major companies like Google, Microsoft, and Meta are heavily investing in the technology and building their own offerings. With the advent of advanced technologies like LLMs and ChatGPT, the enterprise is set to be transformed in ways we can hardly imagine.
To learn more about the history and future of conversational AI in the enterprise, I highly recommend checking out the Microsoft-hosted webinar on how ChatGPT is transforming enterprise support. It's a great way to stay informed and stay ahead of the curve on this exciting new technology. Follow the link and take your first step toward becoming a conversational AI expert.
Contact Moveworks to learn how AI can supercharge your workforce's productivity.