Table of contents
Everyone is talking about large language models and rightfully so. Large language models are a groundbreaking technology.
Large language models, also referred to as LLMs, are poised to revolutionize how we think about conversational AI for the enterprise and its potential applications. Tech giants like Microsoft, Meta and Google know that large language models are fast becoming essential for people to innovate, automate, and improve the lives of the end user as a whole.
One such example that’s taken the world by storm is ChatGPT, which uses OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) to accomplish tasks in a few seconds that would normally take a human hours or days. The generative AI capabilities alone have spawned countless use cases and business opportunities for those eager to dive-in and learn.
But first, let’s explore large language model basics and their applications in real-world use cases. We’ll cover:
- What large language models are
- Large language model examples
- Large language model strengths and challenges
- Applications of large language models
- How large language models will change businesses
- What the future of large language models looks like
What are large language models?
Large language models (LLMs) are advanced artificial intelligence algorithms trained on massive amounts of text data for the purposes of content generation, summarization, translation, classification, sentiment analysis and so much more. How massive are these datasets? Smaller datasets are composed of tens of millions of parameters, while larger sets extend into hundreds of billions of data points. Depending on the purpose of the large language model (LLM), the training data will vary.
Example datasets and what their purpose include:
- Social media posts: Publicly available social posts can be used to train the model to understand informal language, slang, and online trends, as well as to identify sentiment
- Academic papers: Scholarly articles can be used to understand terminology and technical language, as well as to extract key information
- Web pages: Publicly available web sites can be used to understand writing styles or increase the range of topics a large language model can understand
- Wikipedia: Because of the vast knowledge that Wikipedia houses, this can be used to increase the range of topics a large language model can understand
- Books: Books of various genres can be used to understand different writing styles, storyline development, and narrative structures
You may be asking yourself, how does a large language model produce text in a human-like fashion? Using the above examples, if a model is trained on social media posts and books, it becomes easier for the model to produce text in a human-like fashion because it has a clear understanding of formal and informal language. So in reality, the answers it produces is highly dependent on the training data used.
How do large language models work?
To understand how large language models work, you first need to understand transformer architecture. Transformer architecture is the backbone of the transformer models like GPT and many other prominent models.
The transformer architecture is a neural network architecture that allows for parallel processing and is used by large language models to process data and generate contextually relevant responses. It consists of a series of layers, with each layer consisting of parallel processing components called attention mechanisms and feedforward networks. The attention mechanisms weigh the importance of each word, using statistical models to learn the relationships between words and their meanings. This allows LLMs to process sequences in parallel and generate contextually relevant responses.
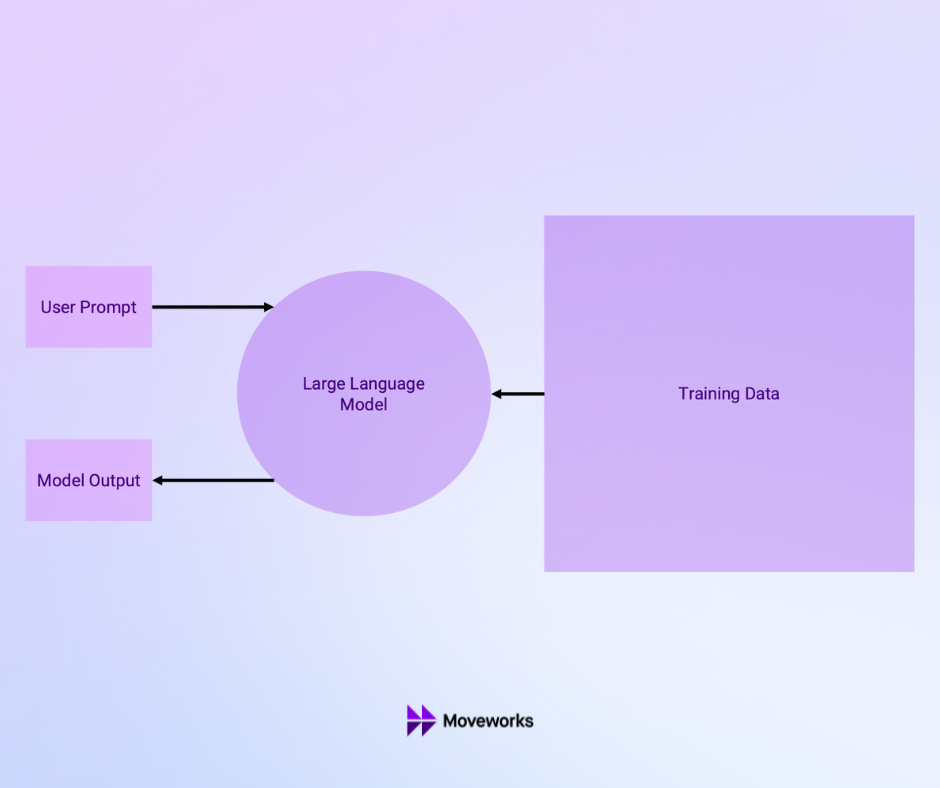 Figure 1: Large language models (LLMs) leverage vast amounts of training data to understand and respond to user prompts conversationally.
Figure 1: Large language models (LLMs) leverage vast amounts of training data to understand and respond to user prompts conversationally.
What are some examples of large language models?
The most talked about models are by OpenAI (GPT-2, GPT-3, GPT-4, Whisper), Google (BERT, T5, PaLM), and Meta (M2M-100, LLaMA, XLM-R). These are some just examples of the most common ones but as stated before, models are trained for specific purposes so there isn’t a single model that does everything.
For example:
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): BERT is a transformer-based model that has been pre-trained on a massive amount of text data. It is designed to perform natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as sentiment analysis, question-answering, and text classification.
- GPT-3 (Generative Pretrained Transformer 3): Developed by OpenAI, GPT-3 is a large language model considered one of the most advanced AI models in the world. It has been trained on a vast amount of text data and can generate human-like responses to a wide range of topics and questions, while maintaining a wide array of conversational memory.
- XLM-R (Cross-lingual Language Model - RoBERTa): XLM-R is a transformer-based large language model developed by Facebook AI Research. It is pre-trained on a massive amount of text data in multiple languages and fine-tuned for specific NLP tasks such as text classification, machine translation, and question-answering.
- Whisper: Whisper is a large-scale automatic speech recognition (ASR) system developed by OpenAI. It is trained on 680,000 hours of diverse and multi-lingual data, resulting in improved robustness to accents, background noise, and technical language. It has the ability to transcribe speech in multiple languages and perform translation into English.
- T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer): Developed by Google Research, T5 is a large language model designed to perform various NLP tasks such as text-to-text generation, summarization, and translation. It utilizes transfer learning to fine-tune its capabilities for specific NLP tasks, making it a highly versatile model.
M2M-100 (Multilingual Machine Translation 100): M2M-100 is a multilingual machine translation model that can translate between any pair of 100 languages without relying on English data. The model is trained on a total of 2,200 language directions, this model is 10 times better than the previous best, English-centric multilingual models.
MPNet (Masked and Permuted Language Modeling Pre-training Network): MPNet is a pre-training method for language models that combines masked language modeling (MLM) and permuted language modeling (PLM) in one view. It takes the dependency among the predicted tokens into consideration through permuted language modeling, advancing BERT's classification methodologies.
When comparing the performance and capabilities of these models, it is important to note that each model has been trained for a very specific purpose, and the best model will depend on the specific NLP task at hand. Large language models have demonstrated impressive performance in various natural language processing tasks and have the potential to greatly enhance businesses' efforts in customer engagement, operations, and beyond.
What are large language models used for?
Large language models are becoming increasingly popular in various industries and businesses because they can process and understand human language at scale. These models use deep learning techniques to analyze vast amounts of text data, making them highly proficient in language processing tasks such as text generation, summarization, translation, and sentiment analysis.
With these capabilities, large language models have revolutionized the field of conversational AI and have a range of real-world applications.
For example:
- Customer Service: They can be used to develop support chatbots that can engage with customers conversationally, improve customer engagement, and drive efficient operations.
- Text Translation: They can also be used in language translation software to accurately translate text from one language to another, making communication and understanding between people who speak different languages much easier.
- Marketing: Models can be used to create ad copy, ad creatives, and even a communication strategy.
- Coding: They can write, optimize or help fix code.
- Healthcare: Language models can help with knowledge retrieval which can help support clinical decision making.
As more large language model applications are developed the companies that are able to harness their true power will be measurable improvements across their organizations.
Why are large language models so important for enterprises?
Large language models represent a transformative technology that can help enterprises access conversational AI and automate mundane tasks that their workforce incurs every day. By leveraging advanced conversational AI capabilities, these models have the potential to deliver unprecedented value to organizations, from curating a superior user experience to reducing costs.
By embracing large language models, enterprises can gain a strategic advantage, remain competitive in a rapidly changing market, and deliver real business value to their customers. It's crucial, however, to have a comprehensive understanding of their complexities to effectively apply them in practical settings.
One of the easiest ways for companies to embrace large language models without incurring significant model development costs is through the integration of an AI copilot. AI copilots are one of the more recent trends where companies are using LLMs to develop chatbot-like interfaces that can support users across the enterprise. Some examples of this are Moveworks’ enterprise copilot, Microsoft’s 365 copilot, Github’s Copilot, and Salesforce’s Einstein. AI copilots will continue to come out as more and more companies build out their use cases so it’s important to have an AI copilot strategy when looking to incorporate them into your organization.
What are large language models' strengths?
Large language models have immense potential for organizations and can bring about a paradigm shift in how they operate.
1. Out-of-the-box advanced natural language processing capabilities
In the past, building a conversational AI required a significant effort from a team of experts who spent countless hours creating multiple machine learning algorithms.
However, the advent of large language models, such as the GPT-3.5 model powering ChatGPT, has changed this landscape. Instead of using multiple algorithms, a single model now performs all the functions previously performed by multiple systems. This has made natural language processing more accessible, as conversing with ChatGPT is now equivalent to having a Swiss watch at your fingertips.
2. Powerful generative capabilities
Language learning models possess a powerful generative capability that makes them valuable assets for the enterprise. With their advanced conversational AI abilities, LLMs can assist businesses in exploring new ideas, developing new products and services, and improving existing ones. The generative abilities of LLMs enable the creation of written content, such as product descriptions, marketing copy, reports, and other digital assets, like images, videos, and software code.
LLMs also can analyze and understand large amounts of data and information, allowing them to provide insightful recommendations to improve business processes and decision-making. Moreover, the conversational interface of LLMs makes it easy for teams to share and collaborate on ideas and projects, increasing productivity and streamlining the creative process.
3. Seamless conversational user experience
Language learning models offer a seamless conversational user experience that is unmatched by traditional AI systems. The enterprise can use this by integrating LLMs into customer-facing applications, such as chatbots, to improve internal communication and support. LLMs can understand user inquiries and provide personalized and efficient support, improving satisfaction.
In IT support, for instance, LLMs can assist with resolving tickets and problems quickly and accurately. Automating certain support tasks conversationally allows businesses to free up valuable resources and focus on more complex issues requiring human expertise.
4. Increased user efficiency
LLMs are equipped to comprehend and process human language, making them suitable for automating monotonous and time-consuming tasks.
For instance, in IT, LLMs can handle simple queries and support requests, allowing human agents to concentrate on more complicated problems. Or in the financial sector, LLMs can automate financial transactions and data processing, reducing the manual effort and resources needed.
LLMs' ability to increase efficiency and lower costs is one of the many reasons they are fast becoming indispensable tools across various industries. By automating tedious tasks, LLMs allow organizations to focus on their core competencies and drive growth and innovation.
What are large language models' challenges?
Understanding large language model nuances is crucial in using them in real-world applications. There are three main large language model weaknesses to consider when thinking about how to apply them practically in business:
1. Inconsistent accuracy
Large language models, including OpenAI's GPT-3.5, are powerful tools that can provide accurate responses to complex questions. However, despite their impressive capabilities, there is still a risk of inaccurate or false responses, known as "hallucination."
This phenomenon can have serious implications in critical industries like healthcare and business operations. It is essential to implement safeguards such as human oversight to refine inputs and control outputs to mitigate this risk. Currently, many applications of large language models require human supervision to ensure reliable results but one promising method that aims to fix this is AI grounding.
2. Lack of enterprise context
Large language models have been trained on a vast amount of text data from the internet. Still, they need enterprise-specific context and domain knowledge to provide specific solutions to industry-specific problems. While they can provide general information and context on various topics, they may not have the depth of understanding and experience required to solve complex, industry-specific challenges.
Additionally, language models may not have access to proprietary information or be aware of the specific regulations and policies that govern a particular industry. As a result, they may only sometimes be able to provide accurate or reliable information in the context of a specific enterprise. It is essential to understand these limitations and seek expert advice when dealing with industry-specific issues.
3. Limited controllability
While language models are powerful and accessible to non-experts, they lack controllability. This means their response to a specific input cannot be easily directed or controlled. The layered approach to building LLMs saves time in training complex systems but limits the ability to control the model's responses in a more demanding environment.
To be effective in a business setting, LLMs must be part of a larger AI architecture that offers control and fine-tuning through additional training, evaluation, and alternative machine learning approaches.
4. Stale training data.
Large language models are trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and respond to natural language in a human-like manner. However, their training data is limited to a specific time period and may not reflect the current state of the world. Updating an LLM's knowledge is complex and requires retraining the model, which is extremely expensive.
Instructing the LLM to override certain parts of its knowledge while retaining others is also challenging. Even then, there's no guarantee that the model won't provide outdated information, even if the search engine it's paired with has up-to-date information. This poses a unique challenge in a business setting where data is often private and constantly changing in real-time.
5. Personal data risk
LLMs are trained on vast amounts of text data, including sensitive personal information, which they may have access to while generating responses. This personal information can be leaked through the model's outputs or training data.
Additionally, the training data used to develop LLMs may not always be properly anonymized or secured, which increases the risk of personal data breaches. The use of LLMs in industries handling sensitive personal information, such as healthcare or finance, requires careful consideration and proper security measures to prevent data leakage.
How exactly will large language models impact the enterprise?
Since ChatGPT launched, it’s given everyone who’s played around with it a sense of wonderment. And what’s even more remarkable is that this is only scratching the surface of what’s possible with generative AI. Large language models aren’t just for writing a quick email — they have the potential to completely transform how work is done, from internal IT and HR support to customer service and marketing ad creation.
Let’s take IT for example.
Large language model applications in IT
1. Language generation
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way IT teams work by streamlining processes and providing new and innovative solutions. From improving knowledge management to automating document creation, the following use cases highlight the many ways in which generative AI can empower IT teams and enhance their workflows:
- Recommend new knowledge articles and forms
- Write net-new knowledge articles and forms
- Update and edit knowledge articles and form
- Translate knowledge articles and forms on the fly
- Write employee comms
- Translate employee comms in real-time
- Translate IT ticket descriptions, common, and work notes
- Write product documentation
2. Language summarization
Generative AI has the potential to greatly enhance the efficiency and productivity of IT support teams by automating tedious and time-consuming tasks. This list of use cases highlights some of the ways generative AI can help surface important analytics, summarize information, and provide quick and accurate solutions for IT ticket topics:
- Extract common topics, symptoms, and sentiments from IT tickets
- Cluster IT tickets by topic
- Auto-generate narratives from analytics
- Summarize IT ticket solutions for agents
- Summarize lengthy IT ticket threads for agents
- Summarize phone support transcripts
- Highlight critical solutions within article snippets
3. Code and data generation
Generative AI can transform IT infrastructure and chatbot development, saving IT agents time by automating time-consuming tasks such as:
- Suggesting conversation flows and follow-up patterns
- Generating training data for conversational AI solutions
- Testing knowledge articles or forms for improved relevance
- Assisting in code generation for repetitive snippets from online sources
What you need to know to navigate the future of large language models
Large language models play a crucial role in the evolution of conversational AI. Their ability to generate human-like language and advanced reasoning skills have impressed both the public and tech companies, who view them as essential platforms for innovation and problem-solving.
Despite the strengths of LLMs, some challenges must be addressed to fully realize their potential, such as hallucination, stale training data, and a lack of enterprise context.
Nevertheless, the future outlook for LLMs and conversational AI remains positive. With the potential for increased efficiency and cost savings, LLMs can revolutionize how organizations operate and interact with customers. It's crucial for leaders across industries and departments to continue exploring and understanding the capabilities of LLMs and to address any limitations to fully harness their potential and shape the future of conversational AI.
Contact Moveworks to learn how AI can supercharge your workforce's productivity.